Miller wants to discourage energy drink purchase, so he's considering a $1 tax or $2 tax on the drink. 1. Is Sen. Miller's plan for a two dollar tax better at stopping consumers from purchasing energy drinks? Why or why not? Incorporate your knowledge of the Laffer Curve in your response.
Miller wants to discourage energy drink purchase, so he's considering a $1 tax or $2 tax on the drink.
1. Is Sen. Miller's plan for a two dollar tax better at stopping consumers from purchasing energy drinks? Why or why not? Incorporate your knowledge of the Laffer Curve in your response.
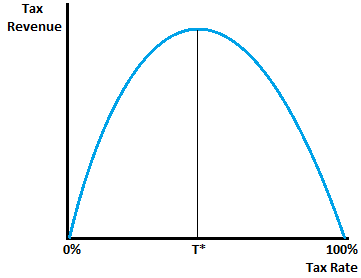
The Laffer curve, given by Arthur Laffer, is a supply-side economics' paradigm that illustrates the relationship between the tax rate levied on economic agents and the tax revenue generated by the taxing authority. It essentially represents the relationship in the form of a curve, the shape of which is a function of taxable income elasticity.
The tax revenue earned by the government on the extreme ends, i.e. a 0% tax rate & 100% tax rate, is zero.
The Laffer curve model argues that an ideal tax rate is derived between the two extreme tax rates as the relationship between the tax rate and tax revenue can be illustrated in the form of an inverted U-shaped curve, indicating an increasing tax revenue when the tax rate is low and decreasing tax revenue when the tax rate goes beyond a certain level.
The rationale behind this is the fact that taxes disincentivize working effort and the higher the tax rate, the more discouraged people become to work and earn. Individuals earn an income and consume from the disposable income left to them after paying their tax obligations. If the tax rate is increased to a very higher level, the incentive to earn income gets eliminated and with it, discretionary consumption which subsequently leads to the eradication of tax revenue.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









