
Concept explainers
Citric acid is responsible for the tartness of citrus fruits, especially lemons and limes.
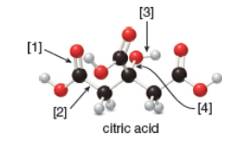
a. What is the molecular formula of citric acid?
b. How many lone pairs are present?
c. Draw a skeletal structure.
d. How many
e. What orbitals are used to form each indicated bond
(a)
Interpretation: The molecular formula of citric acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction: In ball-and-stick model, each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. In this model, each black ball represents
Answer to Problem 40P
The molecular formula of citric acid is
Explanation of Solution
The given ball-and-stick model of citric acid is,
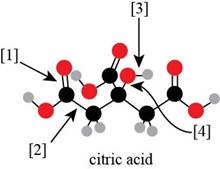
Figure 1
In ball-and-stick model, each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. In this model, each black ball represents
In the above model,
• There are seven red balls. Thus, there are seven
• There are six black balls. Thus, there are six
• There are eight grey balls. Thus, there are eight
Hence, the molecular formula of citric acid is
The molecular formula of citric acid is
(b)
Interpretation: The number of lone pairs present in citric acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction: In a compound or molecule, the lone pairs represent number of unshared electrons on atom. An atom may or may not have unshared electrons. For example, carbon and hydrogen atoms have no lone pair but each oxygen atom has two lone pairs.
Answer to Problem 40P
There are total
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of citric acid is
There are total
(c)
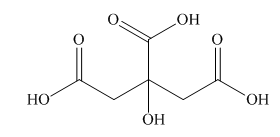
Interpretation: A skeletal structure of citric acid is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: A ball-and-stick model is converted into skeletal structure by replacing black ball with
Answer to Problem 40P
A skeletal structure of citric acid is,
Explanation of Solution
In ball-and-stick model each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. A ball-and-stick model is converted into skeletal structure by replacing black ball with
A skeletal structure of citric acid is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2
In ball-and-stick model each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond.
(d)
Interpretation: The number of
Concept introduction: According to the rule of hybridization, an atom that is surrounded with two groups is
Answer to Problem 40P
There are three
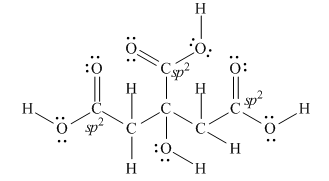
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure of citric acid is,
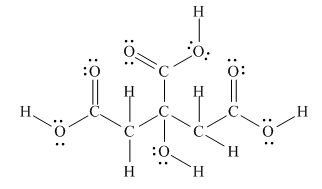
Figure 3
According to the rules of hybridization, an atom that is surrounded with two groups is
The

Figure 4
Thus, there are three
There are three
(e)
Interpretation: The orbitals that are used to form each indicated bond is to be stated.
Concept introduction: According to the rule of hybridization, an atom that is surrounded with two groups is
Answer to Problem 40P
Bond
Explanation of Solution
Bond [1] represents
Bond
Thus,
Bond
Thus,
Bond
The number of surrounded group around any atom predicts the hybridization of that atom, which is further helpful to predict the orbitals involve in bond formation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (6th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (3rd Edition)
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
Chemistry: The Central Science (13th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (3rd Edition)
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- Consider the following computer-generated model of caffeine: Complete a Lewis structure for caffeine in which all atoms have a formal charge of zero (as is typical with most organic compounds). How many C and N atoms are sp2 hybridized? How many C and N atoms are sp3 hybridized? sp hybridized? How many and bonds are there?arrow_forwardAnswer the following questions about amoxicillin, an antibiotic from the penicillin family. a. Predict the hybridization and geometry around each highlighted atom. b. Label five polar bonds using the symbols δ+ and δ–. c. How many π bonds does amoxicillin have? Label them. d. Find a C – H bond containing a carbon atom having a hybrid orbital with 33% s-characterarrow_forwardWhich atomic orbitals overlap to form the carbon-carbon σ and π bonding molecular orbitals of ethene, H2C=CH2? A. C2sp3 + C2sp3, and C2p + C2p B. C2sp2 + C2sp2, and C2sp2 + C2sp2 C. C2sp2 + C2sp2, and C2p + C2p D. C2sp3 + C2sp3, and C2sp2 + C2sp2arrow_forward
- 3. For the following structure answer the following questions CH3 CH-CH₂- 1 CH3 a. Complete the Lewis structure, showing all lone pairs. CH3 1 CH-COOH b. How many carbon atoms are sp, sp2, and sp3 hybridized in the molecule? c. Which hybrid orbitals are used by the two oxygen atoms in the molecule? d. Give approximate values for the bond angles for each angle present in the moleculearrow_forwardAnswer the following questions about acetonitrile (CH3C≡N:). a. Determine the hybridization of both C atoms and the N atom. b. Label all bonds as σ or π. c. In what type of orbital does the lone pair on N reside? d. Label all bonds as polar or nonpolar.arrow_forwardPredict all bond angles in each compound. a. CH3Cl b. NH2OH c. CH2=NCH3 d. HC≡CCH2OHarrow_forward
- Biotin is being studied in a lab. a. What is the IMF(s) of biotin (C10H16N2O3S)? b. What are the sigma/pi bondings and bond angles of biotin? c. What are the resonance functional groups?arrow_forwardCH3+ and CH3− are two highly reactive carbon species. a. What is the predicted hybridization and geometry around each carbon atom? b.Two electrostatic potential plots are drawn for these species. Which ion corresponds to which diagram and why?arrow_forwardVitamin B6 is beneficial to the central nervous system and metabolism. VB6 may improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression, and may promote brain health and reduce Alzheimer's risk. Answer the following questions about VB6. vitamin B6 a. Draw a skeletal structure of vitamin B6 b. How many sp2 hybridized carbons are present? Encircle/highlight them. C. What is the hybridization of the N atom in the ring? Explain.arrow_forward
- Answer the following questions about amoxicillin, an antibiotic from the penicillin family. NH2 H N. N. НО Но amoxicillin a. Predict the hybridization and geometry around each highlighted atom. b. Label five polar bonds using the symbols &+ and 8–. C. How many n bonds does amoxicillin have? Label them. d. Find a C- H bond containing a carbon atom having a hybrid orbital with 33% s-character.arrow_forwardAnswer the following questions about amoxicillin, an antibiotic from the penicillin family. NH2 H N. HO НО amoxicillin a. Predict the hybridization and geometry around each highlighted atom. b. Label five polar bonds using the symbols &+ and &–. C. How many r bonds does amoxicillin have? Label them. d. Find a C – H bond containing a carbon atom having a hybrid orbital with 33% s-character.arrow_forwardB. Answer the next two questions about the Lewis structure of XYZ shown below. メー三 -YEz: I. What is the hybridization of the central atom? II. For all covalent bonds, specify the type of bond (o vs. T) and the atomic orbitals that overlap to form the bond. For example, in a molecule of H2, the only bond is o: H(s)-H(s).arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning



