
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 24.2, Problem 1TH
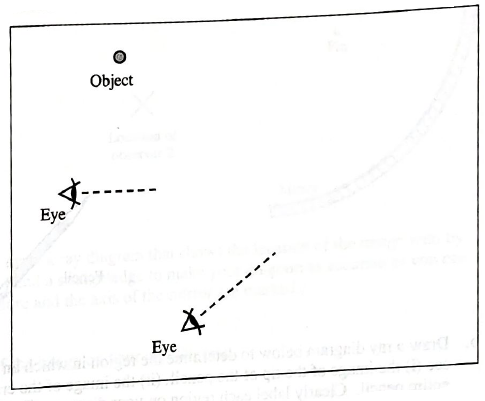
The top view diagrams at right were drawn by a student who is studying image formation by a plane mirror. Each diagram shows the location of an object and two lines of sight to the mirror.
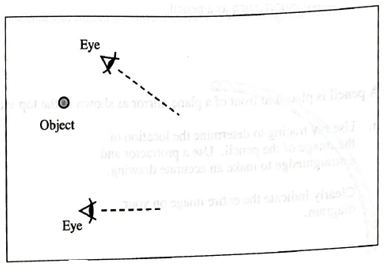
For each diagram, determine whether or not the situation illustrated is possible. If a situation is possible, draw the location and orientation of the mirror.
Explain how you reached your conclusions.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Sketched below are several objects (the arrows labeled "O") in front of lenses. In each case, carefully redraw the sketch on your whiteboard, and then(a) Draw 3 principal rays leaving the top of the object;(b) Locate the image;(c) State whether the image is real or virtual, inverted or upright, and larger or smaller than the object.
(iv) For diagram #iii, suppose the focal length is 5 cm and the object is placed 7 cm from the lens. Find the exact location and magnification of the image. Does this agree with your expectation from the ray diagram?
Show your illustration:
1. A 1-in object is located at the Center of Curvature. Trace and describe the image that will form in a concave mirror if the distance between C and the mirror is 3 inches.
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image distance with object distance in case of a convex lens and answer the question that follow without doing any calculations1) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason in support of your answer2) Write the serial number of that observation which is not correct. How did you arrive at this conclusion.3) Take an appropriate scale to draw ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 4 and find the approximate value of the magnification.Class - 10thChapter - Light, reflection and refraction.
Chapter 24 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 24.1 - On the diagram, sketch what you would see on the...Ch. 24.1 - The small bulb is replaced by three longfilament...Ch. 24.1 - The three longfilament bulbs are replaced by a...Ch. 24.1 - Predict the size and shape of the shadow that will...Ch. 24.1 - Is it possible to place the bulb in another...Ch. 24.1 - Prob. 2cTHCh. 24.1 - Prob. 2dTHCh. 24.1 - Prob. 3aTHCh. 24.1 - A student is looking at the building shown at...Ch. 24.1 - Prob. 4aTH
Ch. 24.1 - Suppose that this student were walking through the...Ch. 24.2 - The top view diagrams at right were drawn by a...Ch. 24.2 - Draw a ray diagram to determine the location of...Ch. 24.2 - Describe how you could use a ray diagram to...Ch. 24.2 - A pencil is placed in front of a plane mirror as...Ch. 24.2 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 24.3 - Prob. 1aTHCh. 24.3 - A pin is placed in front of a semicylindrical...Ch. 24.3 - Prob. 1cTHCh. 24.3 - Prob. 2aTHCh. 24.3 - A very small, very bright bulb is placed for from...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - Prob. 2THCh. 24.4 - Prob. 3aTHCh. 24.4 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 24.4 - Is the image(s) of the nail real or virtual?...Ch. 24.5 - Suppose that the bulb is placed as shown. Using...Ch. 24.5 - Prob. 1bTHCh. 24.5 - Prob. 1cTHCh. 24.5 - Prob. 1dTHCh. 24.5 - Prob. 2aTHCh. 24.5 - Treat the image produced by lens 1 as an object...Ch. 24.5 - Repeat parts a andb for the case in which lens 2...Ch. 24.6 - Reproduced below is a side view diagram of the...Ch. 24.6 - In section III of the tutorial Magnification, you...Ch. 24.6 - Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged...Ch. 24.6 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 24.6 - Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged...Ch. 24.6 - Prob. 3dTHCh. 24.6 - Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
In some countries, liquid nitrogen is used on dairy trucks instead of mechanical refrigerators. A 3.00-hour del...
College Physics
Is it possible to apply a counterclockwise torque to an object thats rotating clockwise? If so, how will the ob...
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Write each number in scientific notation.
1. 326
Applied Physics (11th Edition)
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
BIO Defibrillator During ventricular fibrillation the heart muscles contract randomly, preventing the coordinat...
College Physics
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. Which of the following does inflation ...
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- describe how a ray diagram can be used to show the location of an image formed by a concave mirror. Describe the rays that can be used, where they travel before and after striking the mirror, and where the images form.arrow_forwardA concave lens refracts parallel rays in such a way that they are bent away from the axis of the lens. For this reason, a concave lens is referred to as a diverging lens. Part A: Consider the following diagrams, where F represents the focal point of a concave lens. In these diagrams, the image formed by the lens is obtained using the ray tracing technique. Which diagrams are accurate?(Figure 1) *Type A if you think that only diagram A is correct, type AB if you think that only diagrams A and B are correct, and so on. Part B: If the focal length of the concave lens is -7.50 cm , at what distance d_o from the lens should an object be placed so that its image is formed 3.70 cm from the lens?arrow_forwardThe prism in the diagram is being used as a mirror. (a) Construct a ray diagram to indicate how the light entering the prism travels. Show how it reflects off the back face and also where the reflected ray leaves the prism. (b) Is point A, B, C, D, or E most likely to intercept an outgoing ray? (c) The incoming ray hits the back left face of the prism at what angle? (in terms of the normal to the back face) (d) A reflected ray leaves the back left face of the prism at what angle? (e) What is the index of refraction of the prism if the ray experiences total internal reflection when it hits the back face of the prism?arrow_forward
- The ray diagrams shown trace the path that light takes in order to locate the image formed by a concave mirror. Points C and f indicate the mirror's center center of curvature and focal point. Which ray diagrams are drawn incorrectly.arrow_forwardI don't understand these concepts. Could you please explain each step for this 4 part question? All 4 parts are use the information in the top left of the 1st image.arrow_forwardOn the second image is the formulas. Use the formulas to solve the problem on the first image.arrow_forward
- a convex mirror has a focal length of 1.1 m and the 2.4 m object is 2.6 m away from the mirror. What is the distance, magnification, and height of the image? Show your work.arrow_forwardMIRROR/LENS EQUATION 1. Suppose that the height of the object is 3.00 cm at 20.0 cm from the concave mirror. What are the height and the distance of the image from the mirror if the focal length is 10.0 cm? 2. What is the local length of a convex mirror that produces an image that appears 20.0 cm behind the mirror when the object is 35.0 cm from the mirror? 3. Complete the given table. Show your solution. ( The table is provided in the picture.) Please answer question nos. 1, 2 and 3. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA small object O is placed one-third of the distance between two parallel plane mirrors as in the figure below. (a) Trace appropriate bundles of rays for viewing the four images that lie closest to the object. (b) If the distance between the two parallel plane mirrors is a, then express the distances of these 4 images from the object in terms of the distance aarrow_forward
- A beam of light travels vertically downward and strikes a horizontal mirror, reflecting directly back vertically upward, as indicated by the black dashed line in the diagram at left. The mirror is now rotated, so that it is 10° away from horizontal, as is the red mirror in the diagram . The incident solid black ray is the same in both cases. a) At what angle from the vertical will the reflected beam (the red dashed arrow) now be seen? b) If the mirror is further rotated until it is 20° from the horizontal, what will be the new angle between the reflected beam and the vertical?arrow_forwardA beam of light that consists of a mixture of red, green and violet light strikes a prism(surrounded by air) as shown. Indices of refraction for this prism for the various colorsare indicated in the table. An observer is located to the right of the prism as shown. Determine which color(s) could, in principle, be seen by the observer? Carefully show your work/describe your reasoning.arrow_forwardDraw a ray diagram for each of the following, and then draw the image formed. Please provide complete labels in the diagrams, as well as the size, orientation, type, and position of the image. Thank you so much! You may only opt to answer number 2 if answering all is not allowed:) 1. Object location at 2F’ 2. Object location at F’ 3. Object location beyond 2F’arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
AP Physics 2 - Geometric Optics: Mirrors and Lenses - Intro Lesson; Author: N. German;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=unT297HdZC0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY