
Concept explainers
What can you say about the velocity of a moving body that in dynamic equilibrium? Draw a sketch of such a body using clearly labeled arrows to represent all external forces on the body.
The velocity of a moving body that is dynamic equilibrium and sketch a diagram of such a body.
Answer to Problem 1CQ
The velocity of a body in dynamic equilibrium is a constant, both in magnitude and direction.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
A body is said to be in equilibrium if the total force on the body is zero. On this basis, there are two kinds of equilibria- static equilibrium and dynamic equilibrium. According to Newton's first law, a body continues to be in the state of rest or in the state of uniform motion in a straight line, unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force. Further, Newton's second law implies that an unbalanced force produces an acceleration.
The sum of the forces acting on a body which is in dynamic equilibrium is zero. Therefore, the body experiences no acceleration. As a result, its velocity does not change. Thus, the body which is in dynamic equilibrium moves with a constant velocity.
Consider a block of weight W, acted upon by a force F. The block is placed on a horizontal surface. The surface exerts an upward force FNcalled the normal force on the block. A force of friction f acts between the surface and the block. The block moves towards the right with a velocity v.
The forces W and FNare equal and opposite. Thus, the sum of the forces along the vertical direction is zero. If the applied force F and the force of friction f have equal magnitudes but they are directed opposite to each other. Thus, the net force along the horizontal is also equal to zero. The sum of the forces acting on the block, being zero, the block is not accelerated. Thus, the velocity of the block remains constant. It continues to move with the same speed v and in the same direction.
A diagram representing the forces is shown below.
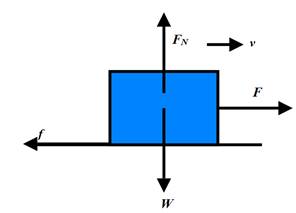
Conclusion:
A moving body under dynamic equilibrium moves with a constant velocity.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
College Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics (10th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
University Physics Volume 2
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
- A student gets his car stuck in a snow drift. Not at a loss, having studied physics, he attaches one end of a stout rope to the vehide and the other end to the trunk of a nearby tree, allowing for a small amount of slack. The student then exerts a force F on the center of the rope in the direction perpendicular to the car-tree line, as shown in the figure below. If the rope is inextensible and if the magnitude of the applied force is 504 N, what is the force on the car? (Assume equilibrium conditions.) KN 12 m Tree 0.50 marrow_forwardA setup similar to the one shown in the figure below is often used in hospitals to support and apply a horizontal traction force to an injured leg. (Let m = 5.25 kg and 8 = 75.0°.) (a) Determine the force of tension in the rope supporting the leg. N (b) What is the traction force exerted to the right on the leg? Additional Materials еВookarrow_forwardA 100 N block is lying along the table top as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the applied force is F= 200 N. If the coefficient of static friction between the surface is 0.30, Calculate the magnitude and direction of the friction force f between the surface that will keep the system in equilibrium. (Express the direction of the friction force in terms of unit vector). 50° 200arrow_forward
- The system shown in figure is in equilibrium. If the static coefficient of friction between the block (m = 1 kg) %3D and the wall is 0.2 and 0 = 30°, the %3D tension in the cord is (in N) m Select one: a. 6.09 b. 8.44 c. 10.35 d. 9.89arrow_forwardThe weightless strut in the figure below is not attached to the wall; it is prevented from falling only by friction. (Let w = 365 N, L = 4.45 m and h = 2.95 m.) (a) Find the magnitude of the force of friction between the wall and the strut.(b) Find the normal force exerted by the wall on the strut.(c) Find the minimum coefficient of static friction.arrow_forwardA 75.0N block sits on a plane inclined 25.0° with the horizontal as shown below. The coefficients of friction between the block and plane are =0.200 and H-0.350. The block is pulled parallel to the incline with a force P as shown. a) What is the smallest force P that will keep the block from slipping down the plane? If the force P is any smaller the block will slip down the plane. b) What is the largest force P for which the block will not slide up the plane? If the force P is any larger the block will slip up the plane. 25.0°arrow_forward
- (a) What is the minimum force of friction required to hold the system of the figure below in equilibrium? Let w, = 120 N and w, = 59.0 N. (b) What coefficient of static friction between the 120 N block and the table ensures equilibrium? (c) If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the 120 N block and the table is 0.295, what hanging weight should replace the 59.0 N weight to allow the system to move at a constant speed once it is set in motion? W2arrow_forwardA thin uniform rod is held against a vertical wall by a cord attached to the end. The rod is not attached at the wall; friction from the wall holds it up. Find the minimum coefficient of static friction to allow equilibrium. Express your answer in terms of the angle θ, and then evaluate for θ = 37deg. Include a free-body diagram and clear explanations with your solution.arrow_forwardConsider the figure below. (Let w, = 150 N and w, = 51.5 N.) W1 W2 (a) What is the minimum force of friction required to hold the system of the figure abdve in equilibrium? N (b) What coefficient of static friction between the 150-N block and the table ensures equilibrium? (Enter the mìnimum acceptable coefficient of friction.) (c) If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the 150-N block and the table is 0.172, what hanging weight should replace the 51.5-N weight to allow the system to move at a constant speed once it is set in motion?arrow_forward
- 4. A 78.5-kg mountain climber, who is 1.63 m tall and whose center of mass is 1.05 m from his feet, climbs down a vertical cliff with his body raised 35.0⁰ above the horizontal (see figure). He holds the rope 1.41 m from his feet and it makes a 22.0° angle with the cliff face. a. b. Find the tension in the rope. Find the horizontal and vertical components of the force that the cliff exerts on his feet. (Treat them like the components of a hinge's force.)arrow_forwardCable AB of the boom truck is hoisting the F = 1960 lb section of precast concrete. A second cable is under tension P, and workers use it to pull and adjust the position of the concrete section as it is being raised. a. Choose the correct free body diagram of hook A, treating it as a particle. Start/End AB 15 F AB 180* - 5*. 301 180*- 5*. 301 115*= 60° 115*= 60° 25 25* Start/End А. В. Start/End AB F AB 180- 5*. 30 180- 5- 301 115 = 60 115 = 60 25" 25 Start/End C. D. The correct diagram is Select v b. Determine P and the tension in cable AB. (Express your answers using three and four significant figures, respectively.) P = lb AB lbarrow_forwardYou are working in an ice skating rink and have been asked to hang a new banner on the wall. Your friend is helping you so that the ladder does not collapse by exerting a force F_AL at an angle ϕ relative to the horizontal. The ladder has a length L and makes an angle of θ with respect to the vertical wall. You have a mass, m_Y, and are a horizontal distance x from the wall. The ladder has a mass of m_L. Because the wall is slick, and the ice on the floor is slick, the frictional forces acting on the ladder are negligible. Find a formula for the magnitude of the force that your friend must exert to keep the ladder from falling, in terms of the following variables: x,L,m_Y,m_L,θ,ϕ. Then use the following values to get a number for the magnitude of F_AL. θ = 30.3 degrees ϕ = 23.028 degrees x = 1.491 meters L = 7.1 meters m_Y = 86.0 kg m_L = 42.14 kg Find the magnitudes of: F_AL, normal force of the wall on the ladder (N_WL), and normal force of the floor on the ladder (N_FL).arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





