
Concept explainers
(Complex Class) Consider class Complex shown in Figs. 10.14-10.16. The class enables operations on so-called complex numbers. These are numbers of the form real Part + imaginaryPart * i. where i has the value
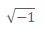
- Modify the class to enable input and output of complex numbers via overloaded >> and << operators, respectively (you should remove the toString function from the class)
- Overload the multiplication operator to enable multiplication of two complex numbers as in algebra.
- Overload the == and t = operators to allow comparisons of complex numbers.
After doing this exercise, you might want to read about the Standard Library’s complex class (from) header <comp1ex>)
- // Fig. 10.14 : Complex.h
- // Complex class definition.
- #include <string>
- #ifndef COMPLEX_H
- #define COMPLEX_H
- Class Complex {
- Public :
- Explicit Complex (double = 0.0, double = 0.0) ; // constructor
- Complex operator+(const Complex&) const; // addition
- Complex operator-(const Complex&) const; // subtraction
- Std:: string toString () const:
- Private:
- Double real : // real part
- Double imaginary ; // imaginary part
- };
- #endif
Fig. 10.14 Complex class deginition.
- // Fig. 10.15 : Complex.cpp
- // Complex class member-function definitions.
- #include <string>
- #include “Complex.h” // Complex class definition
- Using namespace std;
- // Constructor
- Complex: : Complex (double realPart, double imaginaryPart)
- : reak {real Part}, imaginary {imaginaryPart} { }
- // addition operator
- Complex Complex : : operator+ (const Complex& operand2) const {
- Return Complex {real +operand2. Real, imaginary+ operand2. Imaginary};
- }
- // subtraction operator
- Complex Complex : : operator-(const Complex& opetand2) const {
- Return Complex { real − operand 2.real, imaginary − operand2. Imaginary } :
- }
- // return string representation of a complex object in the form: (a, b)
- String Complex : : to String () const {
- Return “(“s +to_string(real) + “, “s + to_string(imaginary) + “)”s;
- }
Fig.10.15 Complex class member-function definition
25 // Fig. 10.16; fig10_16.cpp
26 // Complex class test program.
27 #include <iostream>
28 #include “Complex.h”
29 using namespace std;
30
31 int main () {
32 Complex x:
33 Complex y {4.3, 8,2}:
34 Complex z {3,3, 1,1}:
35
36 count << “x: “ << x.toString () << :\ny: “<<y.to string ()
37 << “\nz: “ <<z:
38
39 x=y+z;
40 count << “\n\nx = y+z:\n” << x.toString () << “= “ << y.toString()
41 << “ + ” <<z.toString ():
42
43 x = y - z :
44 count << “\n\nx = y-z:\n” << x. to String () << “ = “ << y. to String ()
45 << “ - “ << z. toString () << end}:
X: (0, 0)
Y: (4,3, 8,2)
Z: (3,3, 1.1)
X = y+z:
(7.6, 9.3) = (4.3, 8.2) + (3.3, 1.1)
X= y-z :
(1, 7.1) = (4.3, 8.2 ) −(3.3, 1.1)
Fig. 10.16 Complex class test program (Part 2 of 2)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
C++ How to Program (10th Edition)
- (Dynamic Binding vs. Static Binding) Distinguish between static binding and dynamicbinding. Explain the use of virtual functions and the vtable in dynamic bindingarrow_forward(HugeInteger Class) Create a class HugeInteger that uses a 40-element array of digits tostore integers as large as 40 digits each. Provide member functions input, output, add and subtract.For comparing HugeInteger objects, provide functions isEqualTo, isNotEqualTo, isGreaterThan,isLessThan, isGreaterThanOrEqualTo and isLessThanOrEqualTo—each of these is a “predicate”function that simply returns true if the relationship holds between the two HugeIntegers and returns false if the relationship does not hold. Also, provide a predicate function isZero. If you feelambitious, provide member functions multiply, divide and modulus.arrow_forward(Operator Overloads in Templates) Write a simple function template for predicate functionisEqualTo that compares its two arguments of the same type with the equality operator (==) andreturns true if they are equal and false otherwise. Use this function template in a program thatcalls isEqualTo only with a variety of fundamental types. Now write a separate version of the program that calls isEqualTo with a user-defined class type, but does not overload the equality operator.What happens when you attempt to run this program? Now overload the equality operator (withthe operator function) operator==. Now what happens when you attempt to run this program?arrow_forward
- (Java) Q 5,6 Explain the answer step-by-step . I want to understand how to do it so please include verbal explanation. Thank you! Part 1 Write the class described below: The name of the class is Student The class has two public member variables: A String called name and a double called gpa The class has a public member method called printStudent. This method prints out the message: "Hi! My name is " + name + ".\nAnd my gpa is " + gpa It returns nothing Part 2 Now, declare a new Student object named jackie, and assign it the values "Jackie Chan" for the name and 3.5 for the gpa. Finally insert the object jackie into the below ArrayList: ArrayList<Student> al = new ArrayList<Student>();arrow_forward(Complex Class) Consider class Complex shown in Figs. 18.14–18.16. The class enables operations on so-called complex numbers. These are numbers of the form realPart + imaginaryPart* i, where i has the valuea) Modify the class to enable input and output of complex numbers via overloaded >> and<< operators, respectively (you should remove the print function from the class).b) Overload the multiplication operator to enable multiplication of two complex numbersas in algebra.c) Overload the == and != operators to allow comparisons of complex numbersarrow_forward(Enhanced Employee Class) Modify class Employee inFigs. 12.9–12.10 by adding a private utility function calledisValidSocialSecurityNumber . This member function shouldvalidate the format of a social security number (e.g., ###-##-#### , where # is a digit). If the format is valid, return true ;otherwise return false .arrow_forward
- (Modifying Class GradeBook) Modify class GradeBook (Figs. 16.11–16.12) as follows:a) Include a second string data member that represents the course instructor’s name.b) Provide a set function to change the instructor’s name and a get function to retrieve it.c) Modify the constructor to specify course name and instructor name parameters.d) Modify function displayMessage to output the welcome message and course name,then the string "This course is presented by: " followed by the instructor’s name.Use your modified class in a test program that demonstrates the class’s new capabilities.arrow_forward(Time Class Modification) It would be perfectly reasonable for the Time class of Figs. 17.4–17.5 to represent the time internally as the number of seconds since midnight rather than the threeinteger values hour, minute and second. Clients could use the same public methods and get thesame results. Modify the Time class of Fig. 17.4 to implement the time as the number of secondssince midnight and show that there is no visible change in functionality to the clients of the class.[Note: This exercise nicely demonstrates the virtues of implementation hiding.]arrow_forwardPlease pay attention to the required data types in the description. Thetuple, list and vector classes and their objects are not allowed to be used. 1. Define a new C++ class named “PayStub” that manages pay information: number of hours (integer), hourly pay rate (double). The total payout amount will be calculated based on overtime. Any hour that ismore than 40 hours will be paid at 1.5 pay rate. For example, with the hourly pay rate of $10.0 and if the number of hours is 40, the payout amount will be 400 and if the number of hours is 50 it will be (40 * 10)+ (10 * 15) = 550Please note that because the payout is a calculated value, it should not be part of the data members to make the object as small as possible. The class must provide at least the following two methods:• toString method that returns the string containing all the information about the paystub including the total payout amount. For example, here is the output for different paystubs:40 hours at $10.0 an hourHOURS(40)…arrow_forward
- (Enhancing Class Time) Modify the Time class of Figs. 17.4–17.5 to include a tick memberfunction that increments the time stored in a Time object by one second. Write a program that teststhe tick member function in a loop that prints the time in standard format during each iterationof the loop to illustrate that the tick member function works correctly. Be sure to test the followingcases:a) Incrementing into the next minute.b) Incrementing into the next hour.c) Incrementing into the next day (i.e., 11:59:59 PM to 12:00:00 AM).arrow_forwardc++ exercise: 1- Implement the class “cylinder” with member variables radius and height, whichare private of type double. Define the global constant PI=3.1415 and use it incalculating the volume of the cylinder (PI*radius*radius*height).Implement in the class cylinder the following functions:a- A default constructor with default values of one.b- One constructor with two arguments. This constructor should check that thevariable is positive and does not exceed 20, otherwise the variable will beassigned its default value of one.c- A reader for each variable.d- A writer for each variable.e- A reader and a writer for diameter.f- A member function “volume” which calculates the volume of a cylinder.g- A member function “print” which prints the radius, diameter, and height of acylinder.h- A member function display_name() which displays “cylinderarrow_forward(Payroll System Modification) Modify the payroll system of Figs. 20.9–20.17 to includeprivate data member birthDate in class Employee. Use class Date from Figs. 18.6–18.7 to representan employee’s birthday. Assume that payroll is processed once per month. Create a vector of Employee references to store the various employee objects. In a loop, calculate the payroll for each Employee (polymorphically), and add a $100.00 bonus to the person’s payroll amount if the currentmonth is the month in which the Employee’s birthday occurs.arrow_forward
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





