
Program plan:
- Item, start variablesare used for input. There is structure listnode having data, nextPtr member variables which represents the linked list node.
- void insert(node **head, int value) function inserts the node in the a linked list.
- node *concat(node *flist, node *slist) function concat the two linked list and return the resultant linked list.
- void printList(node *head) function display the contents of the linked list.
Program description:
The main purpose of the program is to perform the concatenation of two linked list by implanting the concept which is same as strcat() function of string.
Explanation of Solution
Program:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <alloc.h>
#include <ctype.h>
//structure of node of the linked list
typedefstruct listnode
{
int data;
struct listnode *nextPtr;
} node;
//function to insert a node in a linked list
void insert(node &head,int value);
//recursive function to concate the linked list
node *concat(node *flist, node *slist);
//function to print the content of linked list
void printList(node *head);
//main starts here
void main()
{
int item;
node *flist,*slist;
clrscr();
//initialization of start node of linked list
flist =NULL;
slist =NULL;
//loop to getting input from the user for first linked list
while(1)
{
printf("\nEnter value to insert in a First List: 0 to End ");
scanf("%d",&item);
//check condition to terminate while loop
if(item ==0)
break;
//insert value in a linked list
insert(&flist, item);
}
//loop to getting input from the user for second linked list
while(1)
{
printf("\nEnter value to insert in a Second List: 0 to End ");
scanf("%d",&item);
//check condition to terminate while loop
if(item ==0)
break;
//insert value in a linked list
insert(&slist, item);
}
// print the contents of linked list
printf("\n Content of First List are as follows : ");
printList(flist);
// print the contents of linked list
printf("\n Content of Second List are as follows : ");
printList(slist);
//call the function to reverse the linked list
// and store the address of first node
flist = concat(flist, slist);
//print the contents of concated list
printf("\n Concatenated List contents are as follows : ");
printList(flist);
getch();
}
//function definition to insert node in a linked list
void insert(node &head,int value)
{
node *ptr,*tempnode;
//memory allocation for the new node
ptr = malloc(sizeof(node));
//copy the value to the new node
ptr->data = value;
//set node's pointer to NULL
ptr->nextPtr =NULL;
//if the list is empty
if(*head ==NULL)
//make the first node
*head = ptr;
else
{
//copy the address of first node
tempnode =*head;
//traverse the list using loop until it reaches
//to the last node
while(tempnode->nextPtr !=NULL)
tempnode = tempnode->nextPtr;
//make the new node as last node
tempnode->nextPtr = ptr;
}
}
//function defintion to concat the list
node *concat(node *flist, node *slist)
{
node *ptr;
//check if list is empty
if(flist ==NULL|| slist ==NULL)
{
printf("\none of the lists is empty");
//return the node
returnNULL;
}
else
{
//store first node address
ptr = flist;
//traverse list until last node is not encountered
while(ptr->nextPtr !=NULL)
ptr = ptr->nextPtr;
//store the address of first node of second list
ptr->nextPtr = slist;
}
//return new list
return flist;
}
//function definition to display linked list contents
void printList(node *head)
{
node *ptr;
//stores the address of first node
ptr = head;
//traverse the list until it reaches to the NULL
while(ptr !=NULL)
{
//print the content of current node
printf("%d ", ptr->data);
//goto the next node
ptr = ptr->nextPtr;
}
}
Explanation:In the above code, a structure is created which represents the node of the linked list. Two starting nodes are initialized which contains the address of first node of each list. User is asked to enter the values for first linked list and linked list is created using insert() function by passing the starting pointer and value. This process is repeated to create the second linked list. printList() function is used to display the contents of both lists. Both lists are concatenated using the concat() function by passing the both list. In this function first list is traversed up to last node and then last node pointer points to the first node of second list. Starting node address is returned and stored in the pointer. Finally, concatenated list is displayed using printList() function.
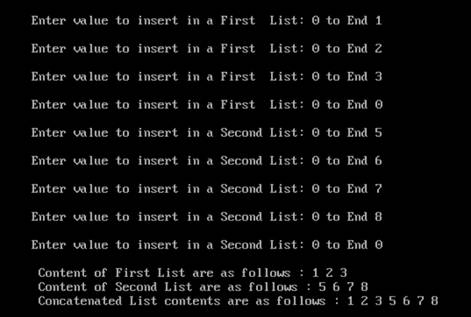
Sample output:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
C How to Program (8th Edition)
- C++ Programming. Theme: Standard string manipulation functions - string concatenation, comparison, character search, string search, replacement and deletion. Task : Given a line(string) of type String . Write a program that arranges its elements in an array of type char A in alphabetical order and in an array of type byte B in ascending order.arrow_forwardC++ PROGRAMMING (Linked list) complete the functions: You have to continue on implementing your Array List namely the following functions: Example ArrayList: [10, 30, 40, 50] void addAt(int num, int pos) This method will add the integer num to the posth position of the list. Performing addAt(20, 2) in the example list will add 20 at the 2nd position and the array will now look like this: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] When the value of pos is greater than the size + 1 or less than one, output "Position value invalid" void removeAt(int pos) Removes the number in the posth position of the list. Performing removeAt(3) in the example list will remove the 3rd element of the list and the updated array will be: [10, 30, 50] When the value of pos is greater than the size or less than one, output "Position value invalid" My incomplete code: #include <cstdlib>#include <iostream>using namespace std; class ArrayList : public List { // : means "is-a" / extend int* array; int index;…arrow_forwardTopic: Singly Linked ListImplement the following functions in C++ program. Read the question carefully. Below are the "CODE THAT NEEDS TO BE IMPROVED" or "NOT FINAL CODE" (See attached photo for reference) int add(int num) This will add the element num into the linked list and return the position of the newly-added element. In the above example, having add(60) will return 5 as it is the fifth position in the list. int remove(int num) This will remove the first instance of the element and return the position of the removed element. In the above example, having remove(40) will return 3 as 40 was the third element in the linked list before having removed. int get(int pos) This method will get the element at the specified position. This will return -1 if the specified position is invalid. int add(int num) { addTail(num); return index; } int remove(int num) { node* currnode = head; node* prevnode = NULL;…arrow_forward
- Pointer Activity You do not need getopt for this program as there are no arguments. Call the executable pointers. Create variables for a character, a string, an integer, and a floating point number. Create pointers for each of those variables. Ideally, use the same name as the variable but add a p in front of the name. (For example: (total and ptotal) Ask the user to enter information for each of these variables one at a time. For each variable tell them what they should enter. (For example: “Enter a single character” or “Enter a floating point number”) Read in the information and put it in the variables. Make each pointer point to the respective variable. Print out values for the four variables without using the variables themselves. Only use the pointers. In addition print out the addresses of the memory locations that each pointer points to. You can use %p for that. Output should look like the bottom sample. Copy and paste the code and the output into a Word document and submit.…arrow_forward(True/False): Local variables are created by adding a positive value to the stack pointerarrow_forwardComplete/Modify the code satisfying the following: (put comments pls) in C++, pls put COMMENTS in the code 1. Create a 10x10 matrix using rand function to fill the said matrix with random numbers 2. Print all the numbers in matrix form 3. Ask the user the following options OPTIONS: A. Total sum, average, median per row B. Total sum, average, median per column C. Display the same matrix but all ODD numbers are replaced with "-" (minus sign) D. Display the same matrix but all EVEn numbers are replaced with "+" (plus sign E. Display the same matrix but all PRIME numbers are replaced with "*" (asterisksign) F. Display the whole matrix with every row in ascending order G. Display the whole matrix with every row in descending order H. Display the whole matrix with every column in ascending order I. Display the whole matrix with every cloumn in descending order J. Generate new set of random numbers Q. Close the program After asking what option to display, Display again the previous numbers…arrow_forward
- .“Dangling and wild pointers are known to be problems with pointers”. Justify the given statement with the helpof suitable examplearrow_forwardprogram Credit Card Validator - Takes in a credit card number from a common credit card vendor (Visa, MasterCard, American Express, Discover) and validates it to make sure that it is a valid number (look into how credit cards use a checksum) - it's a C++ program so use #include <iostream> - And please use an array, use files, and use pointers in this program. -arrow_forwardC++ Programming. OVERVIEW OF DATA STRUCTURES. Task: Write a program to process a data array. Execute a custom task as a separate function or method of a custom class. When performing a task, use functional methods for manually entering array elements, generating random numbers, and printing array elements. Given an array of size N. Create a function to determine the element that is furthest from the arithmetic mean of the array elements (that is, the maximum absolute difference).arrow_forward
- Create a c++ shopping cart program using: linked list- - this will be used as the customer's cart. This is where the items that the customer will buy are placed before checking them out. Array - to store your store products. Pointers - since you will be using linked lists, it is imperative that you also will be using pointers. Functions - Make sure that your program will have user-defined functions (e.g.: function for adding nodes, function for displaying the cart, etc.) The menu options would be coutarrow_forwardC++: (using searching, sorting, and algorithm analysis) Write an application that allows a high school senior to choose their top 5 college choices and store them in an array of strings. The program should use a function to display the unsorted array of colleges. Then use a function to sort the colleges in ascending order then a function to display the sorted array.arrow_forwardC++ Coding: ArraysTrue and False Code function definitions for eoNum() and output(): Both eoNum() and output() are recursive functions. output() stores the even/odd value in an array. Store 0 if the element in the data array is even and store 1 if the element in the data array is odd. eoNum() displays all the values in an array to the console.arrow_forward
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





