
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (MindTap Course List)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781305117396
Author: Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 4FIO
Figure 2.17 Fatty acids.
Double bonds in the tails are highlighted in red.
- A. The tail of stearic acid is fully saturated with hydrogen atoms.
- B. Linoleic acid, with two double bonds, is unsaturated. The first double bond occurs at the sixth carbon from the end of the tail, so linoleic acid is called an omega-6 fatty acid. Omega-6 and
- C. omega-3 fatty acids are “essential fatty acids,” which means your body does not make them and they must come from food.
- D. The hydrogen atoms around the double bond in oleic acid are on the same side of the tail. Most other naturally occurring unsaturated fatty acids have these cis bonds.
- E. Hydrogenation creates abundant trans bonds, with hydrogen atoms on opposite sides of the tail.
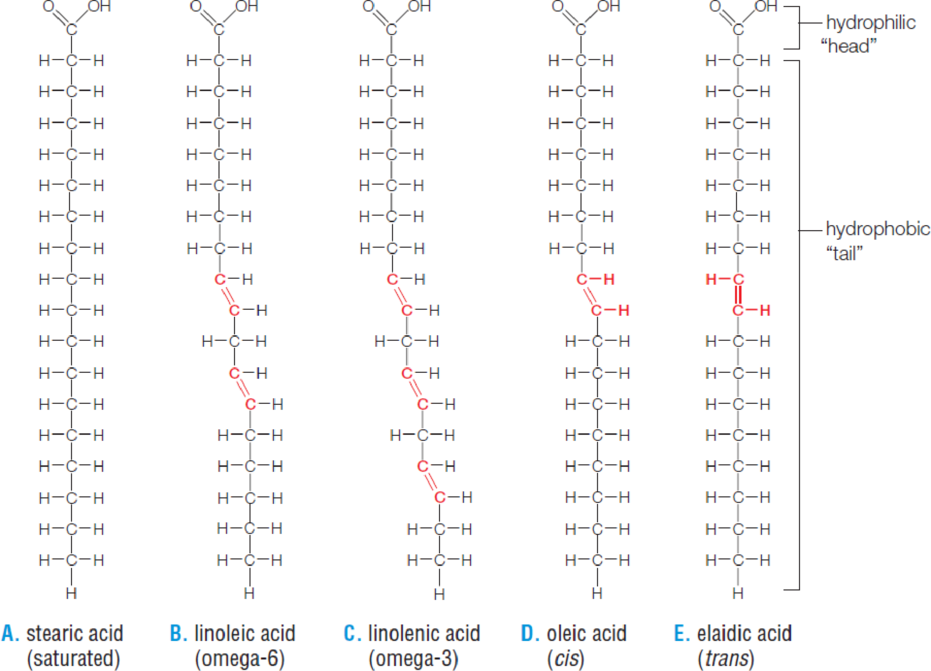
Figure It Out: Are the double bonds in linolenic acid cis or trans?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A. Identify the following fatty acids present in fats and oils by their common names.
Acid
Common name
1.
HO-
H;C (CH2);0-
2.
H3C (CH2)12-
-OH
H,C (CH2)14-Ö-OH
3.
H,C (CH2)16-
-OH
4.
H3C(CH2)18
-HO-
5.
6. Which of the above is the most abundant fatty acid?
7. What is the general formula of a saturated fatty acid?
Consider the fatty acid.
Which of the designations are accurate for the fatty acid?
4,7,10,13-nonadecatetraenoic acid
@-6 fatty acid
20:4(46,9,12,15)
20:4(45,8,11,14)
@-3 fatty acid
Long explanations are not needed. Answers and brief descriptions would be enough.
During the formation of the peptide bond which of the following takes place?
a. Hydrogen atom is lost from its carboxyl group of one amino acid and a hydrogen atom is lost from the amino group of another amino acid.
b. Hydrogen atom is lost from its carboxyl group of one amino acid and a hydroxyl group is lost from the amino group of another amino acid.
c. Hydroxyl group is lost from its carboxyl group of one amino acid and a hydroxyl group is lost from the amino group of another amino acid.
d. Hydroxyl group is lost from its carboxyl group of one amino acid and a hydrogen atom is lost from the amino group of another amino acid.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 2 - A. The first shell corresponds to the first energy...Ch. 2 - B. A chlorine atom (Cl) becomes a negatively...Ch. 2 - Figure 2.12 A pH scale. Here, red dots signify...Ch. 2 - Figure 2.17 Fatty acids. Double bonds in the tails...Ch. 2 - Effects of Dietary Fats on Lipoprotein Levels...Ch. 2 - Effects of Dietary Fats on Lipoprotein Levels...Ch. 2 - Effects of Dietary Fats on Lipoprotein Levels...Ch. 2 - Prob. 1SQCh. 2 - Which element has only one proton?Ch. 2 - The mutual attraction of opposite charges holds...
Ch. 2 - A salt does not release __________ in water. a....Ch. 2 - A(n) _______ substance repels water. a. acidic b....Ch. 2 - When dissolved in water, a(n) _____ donates H+ and...Ch. 2 - _________ is a monosaccharide. a. Glucose b....Ch. 2 - Unlike saturated fatty acids, the tails of...Ch. 2 - Which of the following is a class of molecules...Ch. 2 - Prob. 10SQCh. 2 - Prob. 11SQCh. 2 - Prob. 12SQCh. 2 - Prob. 13SQCh. 2 - Match the molecules with the best description.Ch. 2 - Match each molecule with its component(s).Ch. 2 - Alchemists were the forerunners of modern-day...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2CTCh. 2 - Polonium is a rare element with 33 radioisotopes....Ch. 2 - In the following list, identify the carbohydrate,...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Directions: Draw each structure of the following fatty acid indicated below. 5. Polyunsaturated fatty acid with 18 carbon atoms and three double bonds.arrow_forwardFill in the blanks. The parentheses are the choices for the blank. ______ (Saturated fatty acids, Unsaturated fatty acids). are fatty acids with only single bonds linking the carbons in its tail. A ______ (triglyceride, steroid, phospholipid) is a lipid with three fatty acid tails bonded to a glycerol.arrow_forwardDirections: Draw each structure of the following fatty acid indicated below. 3. Polyunsaturated fatty acid with 14 carbon atoms.arrow_forward
- An illustration of a simple triacylglycerol is given. Choose which type of fatty acid is described by each of the given phrase Choices: A, B, C (Refer to picture) 1. a hydrocarbon chain that bends once 2. a polyunsaturated fatty acid chain 3. cannot be saturated by vitamins 4. absorbs the highest number of iodine 5. can be completely saturated by an I2 moleculearrow_forwardThe structure of a vitamin is shown below. H HH H. нн C C-H H H но нн H Identify two potentially nucleophilic atoms and two potentially electrophilic atoms in your structure, giving a very brief explanation in each case. 2.arrow_forwardCH2OH OH CH2-O-HC H. OH H. CH3(CH2)15-C-NH-CH CH-OH OH H. CH3(CH2)12-CH=CH Download Image... The lipid without the monosaccharide moiety is O A. 1,2-Diacylglycerol O B. 1,2-Diacylsphingosine OC. Sphingosine O D.Ceramide エーCarrow_forward
- Directions: Draw each structure of the following fatty acid indicated below. 2. Monounsaturated fatty acid with 14 carbon atoms.arrow_forwardA. Which of the following is a non-reducing sugar? Isomaltose (B) Maltose (C) Lactose (D) Trehalosearrow_forward1. The figure below shows the Fischer projection of an L-aldohexose. T or F O. НО H- Но H- Но- ČH2OH Naturally occurring saturated long-chain fatty acids are usually in trans- configuration. 2. T or F 3. N-acetylglucosamine is commonly found in glycosaminoglycans. T or F 4. The isoelectric point of isoleucine is lower than that of histidine. T or F 5.. At pH 7, all amino acids stop migrating in isoelectric focusing. T or F 6. The following amino acid is a L-valine. T or F СООН H-NH2 CH-CH3 CH3 7. Salting out is a process to remove salts from proteins. T or F 8. There are five carbons in a pyranose ring. T or F 9. Hydrophobic interaction can be found in protein and DNA. T or F RNA is a polymer consisting of nucleosides joined together by phosphodiester bonds. 10. T or F 11. There are 3.6 base pairs in one turn of DNA helix. T or Farrow_forward
- Three fatty acids are shown below. A онн Но-с-С H H H H H H. H. H. H. нн нннн ċ-Ć -H H H C с-с-н H H H но-с-с-с-с-с нннн ннн нннн Which fatty acid(s) is(are) saturated? Select all that apply. A В C I-O-I エームーエarrow_forwardH. N-C-C Choose A if the statement is CORRECT B if the statement is WRONG H он CH, This amino acid is/has: CH2 6. polar CH2 | CH2 | NH, _7. charged 8. basic side chain 9. aromatic side chain 10. Karrow_forwardA peptide bond... is a version of an ester bond is a version of an amide bond is the basis of protein secondary structure is formed by addition of waterarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Macromolecules | Classes and Functions; Author: 2 Minute Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V5hhrDFo8Vk;License: Standard youtube license