
Engineering Electromagnetics
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780078028151
Author: Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 9.7P
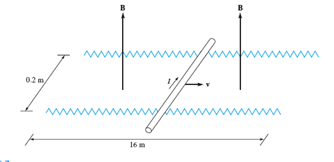
The rails in Figure 9.6 each have a resistance of 2.2
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The magnetic flux through a metal ring varies with time t according to
OB = 5(at3 – bt²)T · m², with a = 1.00 s-3 and b = 6.00 s-2 .
The resistance of the ring is 5.00 N. Determine the maximum current
induced in the ring during the interval from t = 0 to t = 2.00 s. Give
your answer in A.
In the figure below, the rolling axle, 2.90 m long, is pushed along horizontal rails at a constant speed v = 12.00 m/s. A resistor R = 0.4000 N is connected to the rails at points a and b, directly opposite each
other. The wheels make good electrical contact with the rails, so the axle, rails, and R form a closed-loop circuit. The only significant resistance in the circuit is R. A uniform magnetic field B = 0.0300 T is vertically
downward.
B
b.
(a) Find the induced current I in the resistor.
A
(b) What horizontal force F is required to keep the axle rolling at constant speed?
N
(c) Which end of the resistor, a or b, is at the higher electric potential?
O Point a is at a higher potential.
Point b is at a higher potential.
O Point a and point b are at equal potentials.
(d) After the axle rolls past the resistor, does the current in R reverse direction?
O Yes
No
Which of the following configurations can be used to apply Ampere's
circuital law ?
f the length of a solenoid is doubled but the number of turns is halved,
the magnetic field inside will
Ɔ cut by 1/2
Ɔ cut by 1/4
Ɔ Quadrable
Ɔ Double
A
B
None of the above
C
D
...
...
O Only A
Only A & B & C
....
....
... .
Only D
O All of them
None of the above
Chapter 9 Solutions
Engineering Electromagnetics
Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.1PCh. 9 - Prob. 9.2PCh. 9 - Prob. 9.3PCh. 9 - A rectangular loop of wire containing a...Ch. 9 - The location of the sliding bar in Figure 9.5 is...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.6PCh. 9 - The rails in Figure 9.6 each have a resistance of...Ch. 9 - A perfectly conducting filament is formed into a...Ch. 9 - A square filamentary loop of wire is 25 cm on a...Ch. 9 - (a) Show that the ratio of the amplitudes of the...
Ch. 9 - Let the internal dimensions of a coaxial capacitor...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.12PCh. 9 - En free space it is known that E = E0/r sin...Ch. 9 - A voltage source V0, sin cot is connected between...Ch. 9 - Use each of Maxwells equations in point form to...Ch. 9 - Derive the continuity equation from Maxwells...Ch. 9 - The electric field intensity in the region...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.18PCh. 9 - In Section 9.1. Faradays law was used to show that...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.20PCh. 9 - (a) Show that under static field conditions; Eq....Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.22PCh. 9 - Prob. 9.23PCh. 9 - A vector potential is given as A = A0 cos(đ�œ”t =...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.25PCh. 9 - Write Maxwells equations in point form in terms of...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The rod is kept in a magnetic field of B = 0.04IT as shown in the figure. Now if we move the rod at a velocity of v 2.5sin10 t m/sec, then the indued emf in the rod will be %3D Rod X-0.2 O 0.098 V -0.098 V O 0.03 V O ovarrow_forwardA Moving to another question will save this response. Quèstion 11 In ferromagnetic material u= 6µo, B =16y az magnetic strength equals to None of these 4y az /(3µ0) Sy az (3µ0) 2y az /(3µ0) A Moving to another question will save this response. P Type here to search f1 f2 f3 f4 f5 f6 f7 f8 f9 @ $ & %23 2 4. 7 8. Q W- R TY YI U 立 # Marrow_forward3- A magnetic core with an air gap is shown in below Figure. The depth of the core is 3 cm, the length of the air gap in the core is 4 cm, and the number of turns on the coil is 100. How much current is required to produce total flux of 0.00052 Weber? (H= 2000, Ho=4.n107). 6 cm 20 cm N = 100 4 cm = lg 6 cm 6 cm 18 cm 12 cm 18 cm 6 ст Depth = 3 cmarrow_forward
- Consider the magnetic circuit shown in figure u = 2000 HO S2 5 cm/ 1\4 cm 5 сm S2 6 cm If S1= 5 cm? and S2 = 10 cm2 then the total reluctance of the circuit will be 6 cm 14 cm S2arrow_forwardA circular coil of wire with 7 loops and a radius of 0.041 m is placed inside a solenoid. The coil is aligned so that the normal to the coil is parallel to the magnetic field in the solenoid. The solenoid consists of 40000 loops of wire and is 0.18 m long. Initially a current of 0.5 A runs through the solenoid. The current is increased to 4.5 A over a period of 4.1 s. What is the initial magnitude of the magnetic field inside the solenoid?arrow_forwardA coil consists of 100 turns of wire in shape of circle placed in the y-z plane. The loop has an area of 1m² Two magnetic fields linking the surface of the loop: The first one is given by: B1 = -10zt? The second one is B2 = 20ãsin(2w)t emf Select one: a. vm = 0 emf O b. emf 2000t %3D O c. m emf --4000.w.cos(2w)t O d. vm 2000t – 4000.w.cos(2w)t emfarrow_forward
- The circuit in the figure below is located in a magnetic field whose magnitude varies with time according to the expression B = 1.00 x 103 t, where B is in teslas and t is in seconds. Assume the resistance per length of the wire is 0.092 N/m. Find the current in section PQ of length a = 64.0 cm. magnitude HA direction -Select--- P * x x x x x x x * xx x a 2a aarrow_forwardThree point charges are located at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. b. Find the net force on the 2uc charge and -4uc charge 7.00 μC y 60° -4.00 µC 0.50 m +-X 2.00 μCarrow_forwardThe figures below show four arrangements of charged particles, all the same distance from the origin. Rank the situations according to the total (net) electric potential at the origin, most positive first. Remember that potential is a scalar quantity. Carefully explain your reasoning. -24 -24 -4q +2q -24 +29 +24 -9 -94 -39 1-29 1-79 (c) (d) (a) (b)arrow_forward
- In the figure, four long straight wires are perpendicular to the page, and their cross sections form a square of edge length a = 15.0 cm. Each wire carries 7.00 A, and the currents are out of the page in wires 1 and 4 and into the page in wires 2 and 3. In unit-vector notation, what is the net magnetic force per meter of wire length on wire 4? -x Number i i Units Î +arrow_forwardN=15 windings are wound on a square-section iron core with a square outer appearance. If the dimensions are w=2 cm, L1=8 cm and the magnetic permeability of the core is 0.004 H/m, how many micro Henrys is the inductance of the coil? a) 1500 b) none c) 500 d) 0.5 e) 5000arrow_forward2.) Study the circuit on the right. L= 250mH. R, = 500. R2 = 300. E = 12v. a. What is the current in R, the moment the switch S is closed? Ro b. After the switch has been closed for a long time it is opened again. How much magnetic energy is in the inductor 10ms after the switch is reopened?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
The Biot-Savart Law; Author: Jennifer Cash;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1BoIH6Quhiw;License: Standard Youtube License