
Concept explainers
a.
Interpretation:
Given compound has to be labelled as an aldonic acid or alditol.
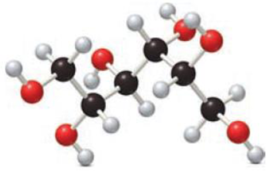
Concept Introduction:
Carbohydrates undergo reduction similar to an
Carbohydrates also undergo oxidation. Monosaccharides that are aldoses contains an
b.
Interpretation:
Given compound has to be labelled as an aldonic acid or alditol.
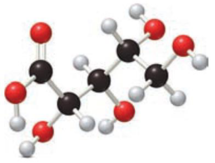
Concept Introduction:
Refer part “a.”.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Principles of General, Organic, Biological Chemistry
- Why is it safe for us to consume foods like vinegar that contain acetic acids?arrow_forwardEthyl butyrate, CH3CH2CH2CO2CH2CH3CH3CH2CH2CO2CH2CH3, is an artificial fruit flavor commonly used in the food industry for such flavors as orange and pineapple. Its fragrance and taste are often associated with fresh orange juice, and thus it is most commonly used as orange flavoring. It can be produced by the reaction of butanoic acid with ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst (H+H+): CH3CH2CH2CO2H(l)+CH2CH3OH(l)H+⟶CH3CH2CH2CO2CH2CH3(l)+H2O(l) Part A Given 7.30 gg of butanoic acid and excess ethanol, how many grams of ethyl butyrate would be synthesized, assuming a complete 100%% yield? Express your answer in grams to three significant figures. Part B A chemist ran the reaction and obtained 5.95 gg of ethyl butyrate. What was the percent yield? Express your answer as a percent to three significant figures. Part C The chemist discovers a more efficient catalyst that can produce ethyl butyrate with a 78.0%% yield. How many grams would be produced from 7.30 gg of…arrow_forwardDraw hexanoic acidarrow_forward
- Ethyl butyrate, CH3CH2CH2CO2CH2CH3CH3CH2CH2CO2CH2CH3, is an artificial fruit flavor commonly used in the food industry for such flavors as orange and pineapple. Its fragrance and taste are often associated with fresh orange juice, and thus it is most commonly used as orange flavoring. It can be produced by the reaction of butanoic acid with ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst (H+H+): CH3CH2CH2CO2H(l)+CH2CH3OH(l)H+⟶CH3CH2CH2CO2CH2CH3(l)+H2O(l) Given 8.45 gg of butanoic acid and excess ethanol, how many grams of ethyl butyrate would be synthesized, assuming a complete 100%% yield? Express your answer in grams to three significant figures. A chemist ran the reaction and obtained 5.50 gg of ethyl butyrate. What was the percent yield? Express your answer as a percent to three significant figures. The chemist discovers a more efficient catalyst that can produce ethyl butyrate with a 78.0%% yield. How many grams would be produced from 8.45 gg of butanoic acid and excess…arrow_forwardFenfluramine and phentermine are two components of fen–phen, an appetite suppressant withdrawn from the market in 1997 after it was shown to damage the heart valves in some patients. What products are formed when fenfluramine and phentermine are each treated with acetic acid (CH3CO2H)?arrow_forwardAmino acids such as glycine are the building blocks of large molecules called proteins that give structure to muscle, tendon, hair, and nails. What product is formed when glycine is treated with concentrated HCl? What product is formed when glycine is treated with NaOH?arrow_forward
- Label each of the following structures as a hemiacetal, hemiketal, acetal, ketal, or none of these: a. c. b.arrow_forwardLabel each of the following structures as a cyclic hemiacetal, hemiketal, acetal, ketal, or none of these: a. b. c.arrow_forwardGive the name of a carboxylic acid or carboxylate salt used in each of the following ways: a.As a soap b.As a general food preservative used to pickle vegetables c.As a preservative used in soft drinks d.As a treatment of athletes foot e.As a mold inhibitor used in bread. f.As a food additive noted for its pH buffering abilityarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,



