
Concept explainers
- a. In what three ways does RNA differ from DNA?
- b. Fill in the following sequence in the flow of genetic information, often called the central dogma. Above each arrow, write the name of the process involved.
Figure 17.6 The codon table for mRNA. The three
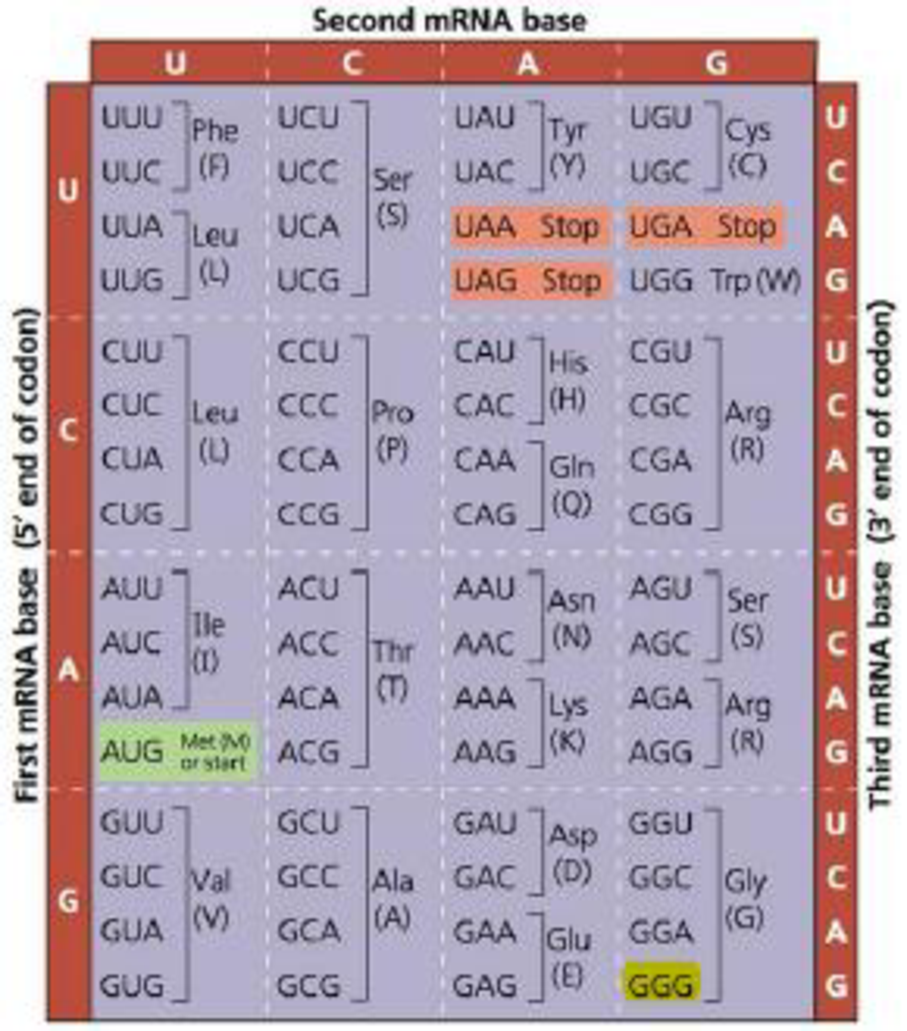
VISUAL SKILLS A segment in the middle of an mRNA has the sequence 5′-AGAGAACCGCGA-3′. Using the codon table, translate this sequence, assuming the first three nucleotides are a codon.
a.
To determine: Three ways in which ribonucleic acid (RNA) differs from deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
Introduction: Nucleic acids are the major organic molecules of all living organisms. Nucleic acids are made of three major components, such as nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and phosphate group. The two major nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA carries the genetic information from one generation to other generation. DNA controls the synthesis of RNA in the cell. RNA is responsible for the synthesis of protein molecules.
Explanation of Solution
Three ways in which DNA differ from RNA are given below:
| Criteria | DNA | RNA |
| Pentose sugar | DNA contains deoxyribose pentose sugar. | RNA contains ribose pentose sugar. |
| Nitrogenous base | DNA has 4 nitrogenous bases, namely adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thiamine. | RNA has 4 nitrogenous bases, namely adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil. |
| Strand | DNA is double-stranded. | RNA is single-stranded. |
b.
To fill and name: The given sequence in the flow of genetic information and the process involved in it.
Introduction: The central dogma of biology explains the flow of information from genes to protein by two processes. These two processes are transcription and translation.
Explanation of Solution
The given sequence in the flow of genetic information and the process involved in it is as follows:
Transcription is a process in which a DNA sequence is converted into a functional piece of RNA. In the initiation of transcription, RNA polymerase binds to the sequence of DNA, and then the unbinding of DNA strand takes place. RNA polymerase adds the RNA bases to the DNA that creates a single strand of mRNA. RNA polymerase detaches from the sequence, and the newly formed sequence of mRNA is released into the nuclear fluid, and then it leaves the nucleus.
After the transcription, the newly formed mRNA enters the cytosol. In the cytosol, processed mRNA associates with many ribosomes. The complex of ribosome-mRNA starts the process of translation. At the initiation of translation, anticodons that appear on tRNA attaches with the mRNA codon. This attachment of tRNA and mRNA codon corrects the orientation of newly arrived amino acids. These amino acids are linked together by a peptide bond, and a peptide chain starts to grow.
Transcription is the formation of RNA from a DNA sequence and through the process of translation, protein is formed from the RNA.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
- Given the following mRNA, write the double-stranded DNA segment that served as the template. Indicate both the 5 and the 3 ends of both DNA strands. Also write out the tRNA anticodons and the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the mRNA message. DNA: mRNA: 5-CCGCAUGUUCAGUGGGCGUAAACACUGA-3 protein: tRNA:arrow_forwardA. What amino acid sequence is encoded by the codon sequence AUAAUGGUAACGGUU? B. Suppose the codon sequence AGACACUCUAUUAAA has a single base pair mutation to AGACACUCUUUUAAA. If the old protein sequence was Arg-His-Ser-Ile-Lys, what will be the new sequence encoded by the mutant gene?arrow_forwardGiven the following DNA sequence: 3'-TACTTNGTNCTNTCN-5' where N stands for any nucleotide, give the complementary mRNA sequence. Indicate direction of strand as 3'--> 5' or 5'--> 3' as in the given sequence above. Give the amino acid sequence of your mRNA sequencelin No. 1. Indicate direction of strand as above. Use all lowercase letters, 3-letter name of amino acid separated by a hyphen (-), no spaces in-between.arrow_forward
- a. Use the genetic code provided in class to predict the sequence of protein formed from the following RNA strand. CGCUACAUCUUU b. If a gene mutation results in a frame shift, meaning the RNA sequence being read shifts rover by a base, and the translation machinery codes, instead, using the nucleotide sequence below, what is the amino acid sequence in the resulting portion of protein? GCUACAUCUUUA c. If a gene mutation results in a point mutation, meaning a single nucleotide is converted to a different nucleotide base, and the translation machinery codes, instead, using the nucleotide sequence below, what is the amino acid sequence in the resulting portion of protein? CGCUCCAUCUUU d. Which mutation is more likely to result in a slightly altered, but still functional, protein, the frame shift mutation or the point mutation? Briefly explain your answer.arrow_forwarda. Use the parent strand as a template to synthesize mRNA strand. Describe how the mRNA strand is generated and regulated. Indicate the direction of synthesis. b. Synthesize a polypeptide from the mRNA.arrow_forwardIllustrate the process of translation by providing the correct bases for tRNA strand given the mRNA template strand. (Remember that mRNA has uracil instead of thymine.) Template Strand: GCUAUGUUUarrow_forward
- Consider the mRNA sequence below. Assume that the following mRNA segment has been translated. 5’-UACCGAAUGUCU-3’ Note for letters a and b: Use the three-letter abbreviation of amino acid; separate amino acids with a hyphen: do not include the stop codon. Example: ala-cys-glu a. Using the table of the genetic code, determine the sequence of amino acids. b. If mutation occurs by substitution of the 12th nucleotide with cytidine-5’-monophosphate, what is the resulting amino acid sequence? c. What type of mutation occurred? Choose from same sense, missense and non-sense.arrow_forwardA. In transcription, a region of DNA opens up. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary RNA transcript. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the RNA transcripf in sequence, except that it has uracil (U) bases in place of thymine (T) bases. Given the following piece of messenger RNA (MRNA): CCUGCAGUAUGAAACGCCUGGUAGAAGGUGGGAAGUGGUGCGCC... Answer the following questions. 1. List the complementary non-coding DNA sequence. This refers to the template strand. (Please insert a space every after three letters for easy checking of your papers. Thank you.) 2. List the DNA strand sequence complementary to the template strand. This refers to the coding strand. (Please insert a space every after three letters for easy checking of your papers. Thank you.) 3. List the amino acid sequence of the protein coded for. (Please insert a space every after one amino acid for easy checking of your papers. Thank you.)arrow_forwardCodon chart: We interpret mRNA 3 base pairs at a time. This is known as a codon. A codon table can be used to translate a genetic code into an amino acid sequence. The full set of relationships between codons and amino acids (or stop signals) is called the genetic code. The genetic code is often summarized in a table like the one below. Second letter A G UUU UUC J UGU Cys UCU) UCC UCA UCGJ UAU U Phe Tyr UACS UGCJ Ser UAA Stop UGA Stop A UAG Stop UGG Trp UUA UUG FLeu G CUU ) CỤC CUA CUG CCU ) ССС ССА CCG CGU CGC Arg CAU) CÁC His САА Leu Pro CGA Gin CAG CGG AUU AAU ACU АСC ACA Asn AGU Ser AAC JAsh AGC. AUC le A AUA AGA Arg Thr AAA AAG. }Lys A AUG Met ACG AGG J G GUU GUC G Val GUA GUG GCU) GCC GCA GCG GAU1 GACS GAA) GAG Glu GGU GGC Gly U C A Ala GGA GGG] G First letter UUAG Third letterarrow_forward
- A. The diagram below shows a tRNA molecule. (i) Which part of a cell is the tRNA produced? (ii) Which part of this tRNA molecule (X, Y, Z) is amino acid attached to? Is ATP or GTP required in the formation of this attachment? (iii) Which part of this tRNA molecule (X, Y, Z) binds to mRNA? Name the bond formed at this part of tRNA with mRNA. (iv) Write the sequence of consecutive Z and amino acid sequence corresponding to the following mRNA sequence. 3' AUGCCGUACUAG 5' In your answer, copy the mRNA sequence. Below the mRNA sequence, write the TRNA sequence with 5' & 3' labels (from left to right), AND the amino acid sequence.arrow_forwardBelow is the 5’–3’ strand of a double-stranded DNA molecule with the following nucleotide sequences:5’ C C T A T G C A G T G G C C A T A T T C C A A A G C A T A G C 3’ 1. If the RNA synthesized above (item #1) is a functional mRNA and all the nucleotides belong to an exon,a. how many codons are present in this mRNA?b. how many codons actually code for proteins in this mRNA?c. what stop codon is present in this mRNA?arrow_forward10. A portion of 5'-AUGCCACGAGUUGAC-3'. What amino acid sequence does this code for? To answer the question please: I) explain what is the genetic code and list the properties of the genetic e 2) draw a diagram of protein synthesis; 3) determine which tRNA should be attached to the mRNA; 4) what is the anticodon for the very first tRNA that will attach to mRNA? mRNA molecule has the sequence anarrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

